

The knee joint consists of three bones – femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone) and the patella (knee cap). The knee is a major weight bearing joint that is held together by muscle and ligaments. Cartilage is the material inside the joint that provides shock absorp- tion to the knee during weight bearing activities.
- Lifestyle modifications like losing weight, avoiding aggravating activities
- Exercises to improve strength and flexibility
- Pain killer to provide temporary pain relief
- Joint fluid therapy to improve lubrication in the joint
- Glucosamine / Chondroitin to relieve arthritic pain
- Bracing to provide external stability
- Arthroscopic surgery to remove debris or repair torn cartilage
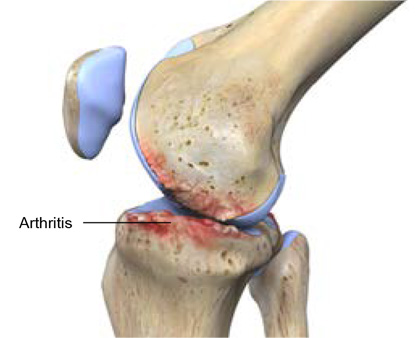
Arthritis in the knee joint occurs as a result of degen- eration of the cartilage in your knee. Due to osteo- arthritis, the cartilage in the knee breaks down over time and the result is severely damaged joint surface with bone rubbing on bone.
In rheumatoid arthritis, it is a chronic inflammatory disease that results in joint pain, stiffness and swell- ing. During the disease process, it causes erosion of the articular cartilage gradually and subsequent damage to the knee joint surface. The disease pro- cess leads to severe and at times rapid deterioration of multiple joints, resulting in severe pain and loss of function.
Total knee replacement surgery is considered when all conservative measures have failed to provide successful intervention which helps to relieve pain, improve joint stability, improve alignment and correct bone deformity, maximize quality of life and optimize activities of daily living.

It is a surgical procedure in which damaged articular ends of thigh bone (femur) and shin bone ( tibia) were replaced by artificially made prosthesis.
Each prosthesis is made up of four parts. The tibial component has two elements which replaces the top of shin bone. This prosthesis is made up of a metal tray attached directly to the bone and a high density plastic spacer that provides the bearing surface. The femoral component replaces the bottom of the thigh bone or femur.
The patellar component replaces the surface of the knee cap which rubs against the femur.
The rehabilitation process following total knee re- placement is very important and can be quiet painful at times. Proper rehabilitation post surgery helps you to achieve the pain free full range of movement in your operated knee.
In the hospital – Ambulation with walker, Range of motion exercises, edema control by ice compression
At home – Begin ambulation with a cane as tolerated and continue home exercise program.
Outpatient Physical therapy – Advanced strengthening program, stationary cycling, walking program, aquatic therapy.
Long term rehabilitation goals – Range of motion from 100 – 120 degrees of knee flexion, Independent with all activities of daily living.
