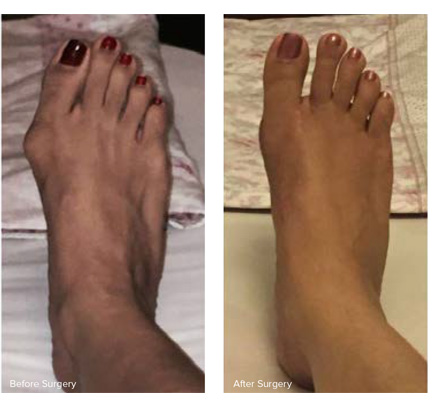
HALLUX VALGUS (BUNION)
- It is a condition characterised by outward deviation of great toe due to various causes and produce a bump on the inside of foot.
- Its common with people who wear high heel with narrow toe box foot wear
- More common in females
- 70% of patients will have family history of similar complaints
- Patient presents with c/o difficulty in wearing shoes, pain over the bump and deformity of the great toe. This condition can be associated with flat foot, lesser toe deformities.
- Weight bearing and oblique view xrays needed to assess the amount of great toe deviation and joint status in great toe and to plan the treatment
- Treatment – Non operative like shoe modification, pads, spacers
- Operative – soft tissue procedure, bony cuts (Osteotomy) or combined both to correct the deformity
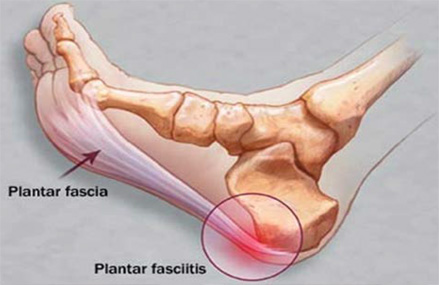
PLANTAR FASCIITIS
- It is a condition in which plantar fascia (a thin layer of connective tissue) gets inflamed near its origin on calcaneum
- Affects men and women equally
- Patient presents with heel pain often when first getting out of bed may prefer to walk on toes initially and worse at the end of the day after prolonged standing, relieved by ambulation
- Xray most often normal, may show plantar heel spur
- Blood investigations to be done to rule out other causes of heel pain like gout, infection
- Treatment – Non operative like pain control, night splint, stretching therapy, short wave treatment
- Operative – Surgical release with plantar fasciotomy

ANKLE SPRAIN
- Most common reason for missed athletic participation
- Most common injury in dancers
- Grade of ankle sprain
- Xray to be done to rule out any bony injuries, ankle instability
- MRI to be considered if pain persists for 8 weeks following sprain to rule out any other cause for pain
- Treatment – Non operative RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), Elastic wrap to minimise swelling
- Operative – In chronic ankle sprain – Modified Brostrom procedure

FLAT FOOT
- It is a condition in which the longitudinal arch in the foot, which runs lengthwise along the sole of the foot, has not developed normally and is lowered or flattened out.
- This condition can affect one or both feet
- You have this condition when your sole makes complete or near complete contact with the ground
- You can get it after an injury or because of health problem, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Most people don’t have symptoms, although weight gain, ill fitting shoes or standing a lot may cause pain in your feet and legs
- Treatment – Non operative orthotic correction and physical therapy
- Operative : Surgical correction of deformity
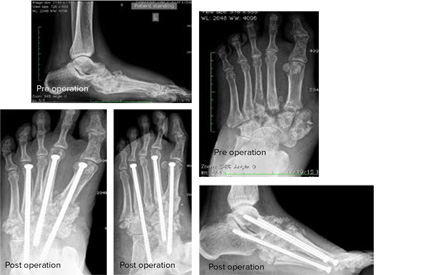
CHARCOT FOOT
- It is a condition in which protective sensation of the joint is lost which results in destruction of joints and surrounding bony structures may lead to amputation if left untreated
- Most commonly seen in diabetic patients
- Patient usually presents with swollen foot and ankle, warmth foot, redness in foot
- Patient also c/o deformed foot, bony prominences, unstable joints
- If bony prominence left untreated may lead to ulcer formation
- Xray needed to assess the amount of joint destruction, subluxation or dislocation of the joints in foot
- Blood test to rule out infection, to detect underlying pathology like diabetes mellitus
- Treatment – Non operative – total contact casting, shoe wear modifications, medications
- Operative – to achieve plantigrade (normal) foot that allows ambulation without skin ulcers
- Resection of bony prominences, Deformity correction, arthrodesis, amputation.

ACHILLES TENDONITIS
- Patient presents with pain backside of the heel may be due to various causes like swelling of Achilles tendon near its attachment to heel bone (calcaneum), inflammation of bursa between Achilles tendon and heel bone (Retrocalcaneal bursitis) or due to bony enlargement on backside of the heel bone (Haglund deformity)
- Patient usually c/o pain on shoe wear, bony bump on the backside of the heel, swelling on either side of the Achilles tendon
- Xray needed to assess any bony spur from calcaneum and any calcium deposit in tendon
- MRI helps to detect the amount of damage to Achilles tendon
- Treatment – Non operative – Activity modification, shoe wear modification like small heel lift
- Operative – removal of diseased portion of tendon, bony bump removal from heel bone, bursa excision
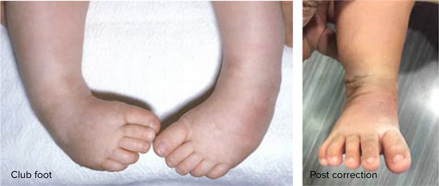
CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS (CLUB FOOT)
- In this condition usually baby will be brought by the parents with c/o deformity of one or both foot pointing downwards and turn inwards.
- Nothing to worry about the condition it is completely correctable
- Treatment – Non operative serial manipulative cast application
- In severe cases surgical procedures like soft tissue release. In resistant cases, ring fixator may be required to achieve full correction
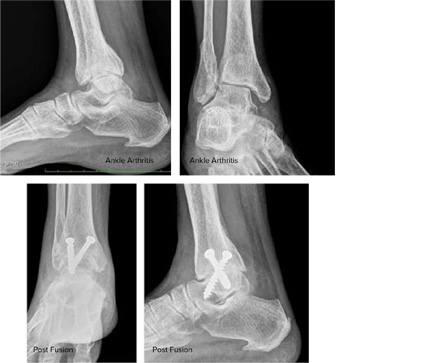
ANKLE ARTHRITIS
- It is a condition in which joint surface of shin bone (tibia) at lower end and talus get degenerated and results in irregular joint surface which alter the load bearing mechanics of the ankle joint
- Damage to joint surface of the ankle joint may happen due to trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, haemophilia
- Patient usually presents with pain with weight bearing, loss of movement in ankle joint, swelling and deformity in ankle joint
- Xray needed to assess the amount of joint space reduction, angular deformity of the ankle joint
- Treatment option – Non operative – activity modification, pain killer, bracing
- In case of failure of conservative management, operative management required in the form of either fusion of the damaged joints (Ankle arthrodesis) or replacement of the damaged joint surface (Ankle replacement)
